A vibration meter is used in inspection, manufacturing and production, and the laboratory.Overview Vibration Meter / Vibration Tester The vibration tester is used to measure vibrations  and oscillations in many machines and installations, as well as in the development of products such as tools or components. Measurements of the vibration meter cover the following parameters: vibration acceleration, vibration velocity and vibration displacement.
and oscillations in many machines and installations, as well as in the development of products such as tools or components. Measurements of the vibration meter cover the following parameters: vibration acceleration, vibration velocity and vibration displacement.
In this way, vibration is recorded with great precision. The vibration tester is a portable device and its readings can be stored and retrieved for later use. Manufacturer's calibration certificates are included with most vibration testing devices.
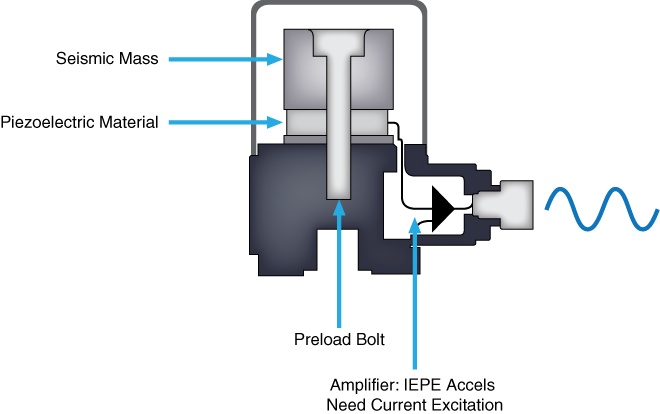
Vibration is most commonly measured using a ceramic piezoelectric sensor or accelerometer. An accelerometer is a sensor that measures the dynamic acceleration of a physical device as a voltage. Accelerometers are full-contact transducers typically mounted directly on high-frequency elements, such as rolling-element bearings, gearboxes, or spinning blades. These versatile sensors can also be used in shock measurements (explosions and failure tests) and slower, low-frequency vibration measurements. The benefits of an accelerometer include linearity over a wide frequency range and a large dynamic range.
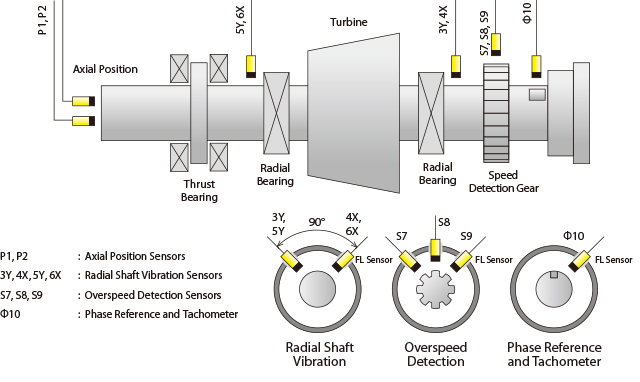
Another sensor you can use to measure vibration is the proximity probe. Unlike accelerometers, which measure acceleration to determine vibration, proximity probes are noncontacting transducers that measure distance to a target. These sensors are almost exclusively used in rotating machinery to measure the vibration of a shaft. An example of a common application is machine monitoring and protection measurements for mechanical systems like turbo machinery. Because of the flexible fluid film bearings and heavy housing, vibrations do not transmit well to the outer casing, so you use proximity probes instead of accelerometers to directly measure shaft motion.